
[ad_1]
Two years after he spoke at a convention detailing his bold imaginative and prescient for cooling tomorrow’s information facilities, Ali Heydari and his crew received a $5 million grant to go construct it.
It was the biggest of 15 awards in Might from the U.S. Division of Vitality. The DoE program, referred to as COOLERCHIPS, acquired greater than 100 purposes from a who’s who record of pc architects and researchers.
“That is one other instance of how we’re rearchitecting the information heart,” stated Ali Heydari, a distinguished engineer at NVIDIA who leads the challenge and helped deploy greater than one million servers in earlier roles at Baidu, Twitter and Fb.
“We celebrated on Slack as a result of the crew is everywhere in the U.S.,” stated Jeremy Rodriguez, who as soon as constructed hyperscale liquid-cooling methods and now manages NVIDIA’s information heart engineering crew.
A Historic Shift
The challenge is bold and comes at a essential second within the historical past of computing.
Processors are anticipated to generate as much as an order of magnitude extra warmth as Moore’s regulation hits the bounds of physics, however the calls for on information facilities proceed to soar.
Quickly, at the moment’s air-cooled methods received’t be capable to sustain. Present liquid-cooling strategies received’t be capable to deal with the greater than 40 watts per sq. centimeter researchers count on future silicon in information facilities might want to dissipate.
So, Heydari’s group outlined a complicated liquid-cooling system.
Their method guarantees to chill an information heart packed right into a cell container, even when it’s positioned in an atmosphere as much as 40 levels Celsius and is drawing 200kW — 25x the facility of at the moment’s server racks.
It’ll value no less than 5% much less and run 20% extra effectively than at the moment’s air-cooled approaches. It’s a lot quieter and has a smaller carbon footprint, too.
“That’s an awesome achievement for our engineers who’re very good people,” he stated, noting a part of their mission is to make folks conscious of the adjustments forward.
A Radical Proposal
The crew’s resolution combines two applied sciences by no means earlier than deployed in tandem.
First, chips can be cooled with chilly plates whose coolant evaporates like sweat on the foreheads of hard-working processors, then cools to condense and re-form as liquid. Second, whole servers, with their decrease energy elements, can be encased in hermetically sealed containers and immersed in coolant.
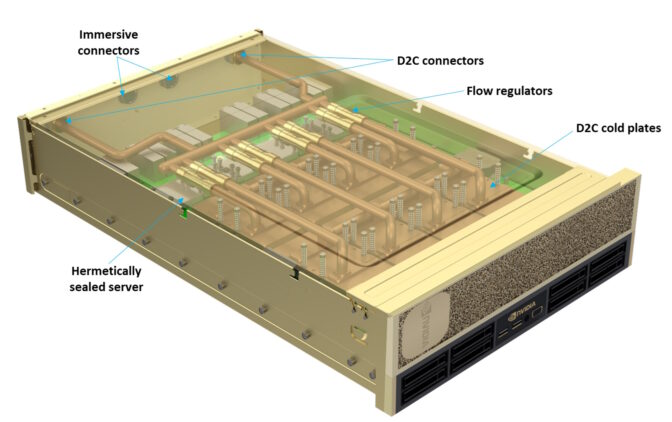
They are going to use a liquid widespread in fridges and automobile air conditioners, however not but utilized in information facilities.
Three Large Steps
The three-year challenge units annual milestones — part checks subsequent 12 months, a partial rack take a look at a 12 months later, and a full system examined and delivered on the finish.
Icing the cake, the crew will create a full digital twin of the system utilizing NVIDIA Omniverse, an open growth platform for constructing and working metaverse purposes.
The NVIDIA crew consists of a few dozen thermal, energy, mechanical and methods engineers, some devoted to creating the digital twin. They’ve assist from seven companions:
- Binghamton and Villanova universities in evaluation, testing and simulation
- BOYD Corp. for the chilly plates
- Durbin Group for the pumping system
- Honeywell to assist choose the refrigerant
- Sandia Nationwide Laboratory in reliability evaluation, and
- Vertiv Corp. in warmth rejection
“We’re extending relationships we’ve constructed for years, and every group brings an array of engineers,” stated Heydari.
In fact, it’s exhausting work, too.
As an example, Mohammed Tradat, a former Binghamton researcher who now heads an NVIDIA information heart mechanical engineering group, “had a sleepless night time engaged on the grant software, nevertheless it’s a labor of affection for all of us,” he stated.
Heydari stated he by no means imagined the crew could be bringing its concepts to life when he delivered a chat on them in late 2021.
“No different firm would enable us to construct a corporation that would do this sort of work — we’re making historical past and that’s superb,” stated Rodriguez.
See how digital twins, inbuilt Omniverse, assist optimize the design of an information heart within the video beneath.
Image at prime: Gathered lately at NVIDIA headquarters are (from left) Scott Wallace (NVIDIA), Greg Strover (Vertiv), Vivien Lecoustre (DoE), Vladimir Troy (NVIDIA), Peter Debock (COOLERCHIPS program director), Rakesh Radhakrishnan (DoE), Joseph Marsala (Durbin Group), Nigel Gore (Vertiv), and Jeremy Rodriguez, Bahareh Eslami, Manthos Economou, Harold Miyamura and Ali Heydari (all of NVIDIA).
[ad_2]